Notice: please copy the notes on bases/alkalis for today
Introduction
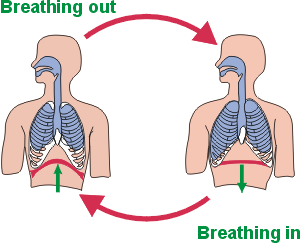
Respiration is the sequence of events that results in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the body cells. Every 3 to 5 seconds, nerve impulses stimulate the breathing process, or ventilation, which moves air through a series of passages into and out of the lungs.
OBJECTIVES:
AFTER COMPLETING THIS TOPIC STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO:
- explain how respiration releases energy in foods for both the use of plants and animals.
- compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- write word equations for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, naming reactants and products.
- compare inhaled and exhaled air using a table format.
Subject Content
Our Sensory Organs and nervous, muscular and skeletal systems
Respiration


