Transport in Plants
- Objectives
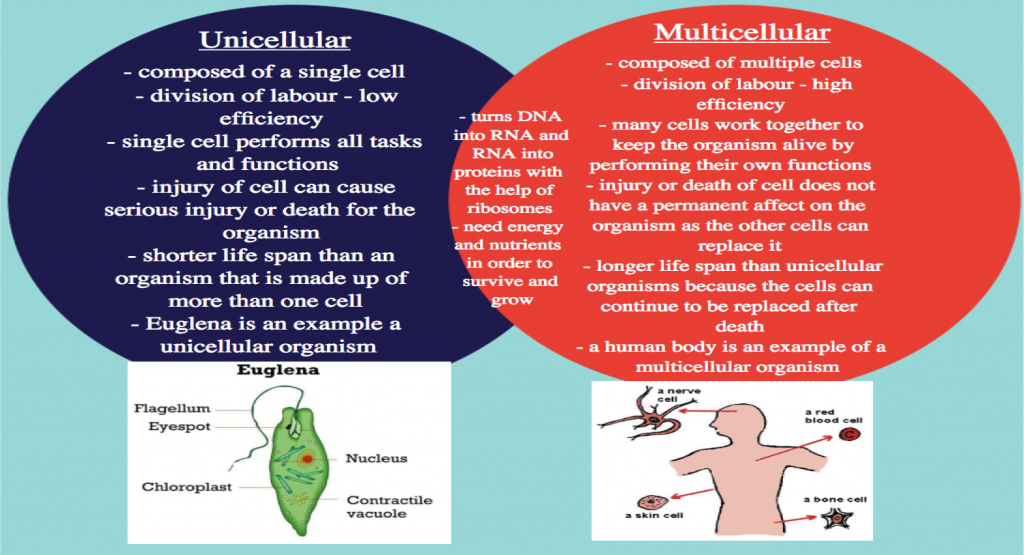
- To contrast the transport system of unicellular organisms vs. multicellular organisms
- To compare the transport system of plants and animals

•Simple organism = simple transport system
•Osmosis and Diffusion
•Osmosis is? 1 point
•Diffusion is? 1 point
•Multicellular organisms need more complex set up to meet the metabolic demand of the body.
•Lungs, gills, skin
•Respiratory surfaces
•What are the properties of good respiratory surfaces? HW
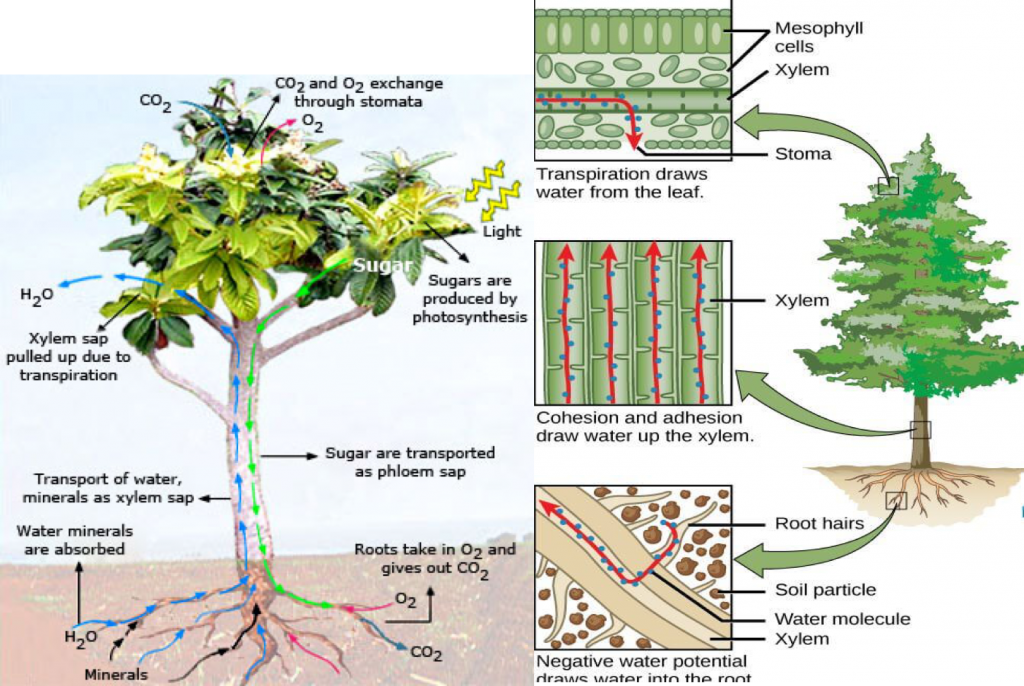

Transport in biology means carrying substance absorbed or made in the body of an organism to all other parts of its body.•In plants, it is only water and minerals that need to be transported to its other parts. Another thing that needs to be transported to other parts of the plants is the food prepared in leaves. This is because a plant has a branching shape so it gets carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and oxygen for respiration from air directly through diffusion.
Plants need water to make food through the process of photosynthesis and minerals for making proteins. Thus, a plant absorbs water and minerals from soil through roots and transport it other parts like stem, leaves, flowers etc. It is through two kinds of elements of xylem tissue called, xylem vessels and tracheid that water and minerals move from roots of a plant to its leaves.
Phloem is a long tube made of many living cells joined end to end. The living cells of phloem are called sieve tubes. The end walls of cells in the phloem have sieve plates which have tiny holes in them. It is through these holes that the food passes along the phloem tubes. Sieve tubes contain cytoplasm in them but have no nucleus. Each sieve tube cell has a companion cell which has a nucleus and many other organelles. The cell wall of sieve tubes contains cellulose but no lignin.
The food is made by the mesophyll cells of a leaf and from there it enters into the sieve tubes of the phloem. These phloem tubes are interconnected and once the food reaches the phloem tube of a leaf, it is then transported to all other parts of a plant.
Forces of adhesion, transpiration? HW



